
Classical Conditioning: Involves pairing a neutral stimulus with a meaningful one to elicit a similar response (e.g., Pavlov’s dogs salivating at the sound of a bell).
Operant Conditioning: Involves learning through rewards or punishments, where behaviors are strengthened or weakened based on their consequences (e.g., Thorndike’s Law of Effect).

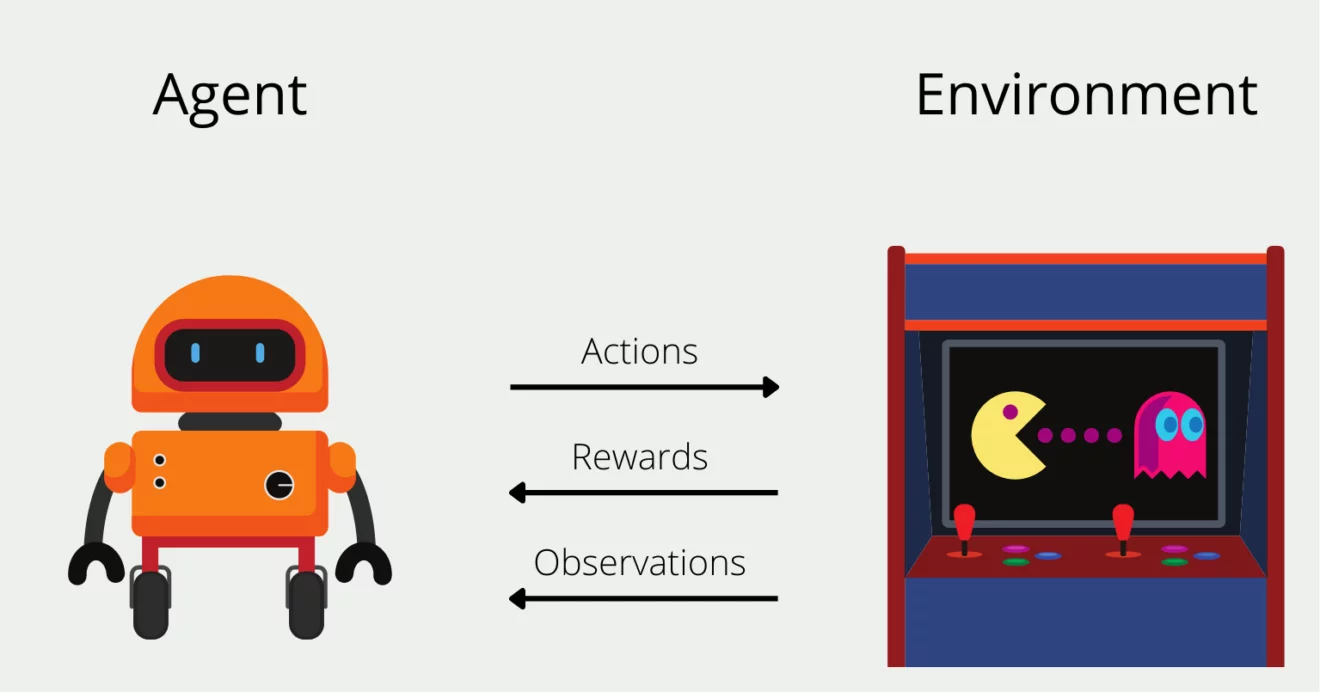
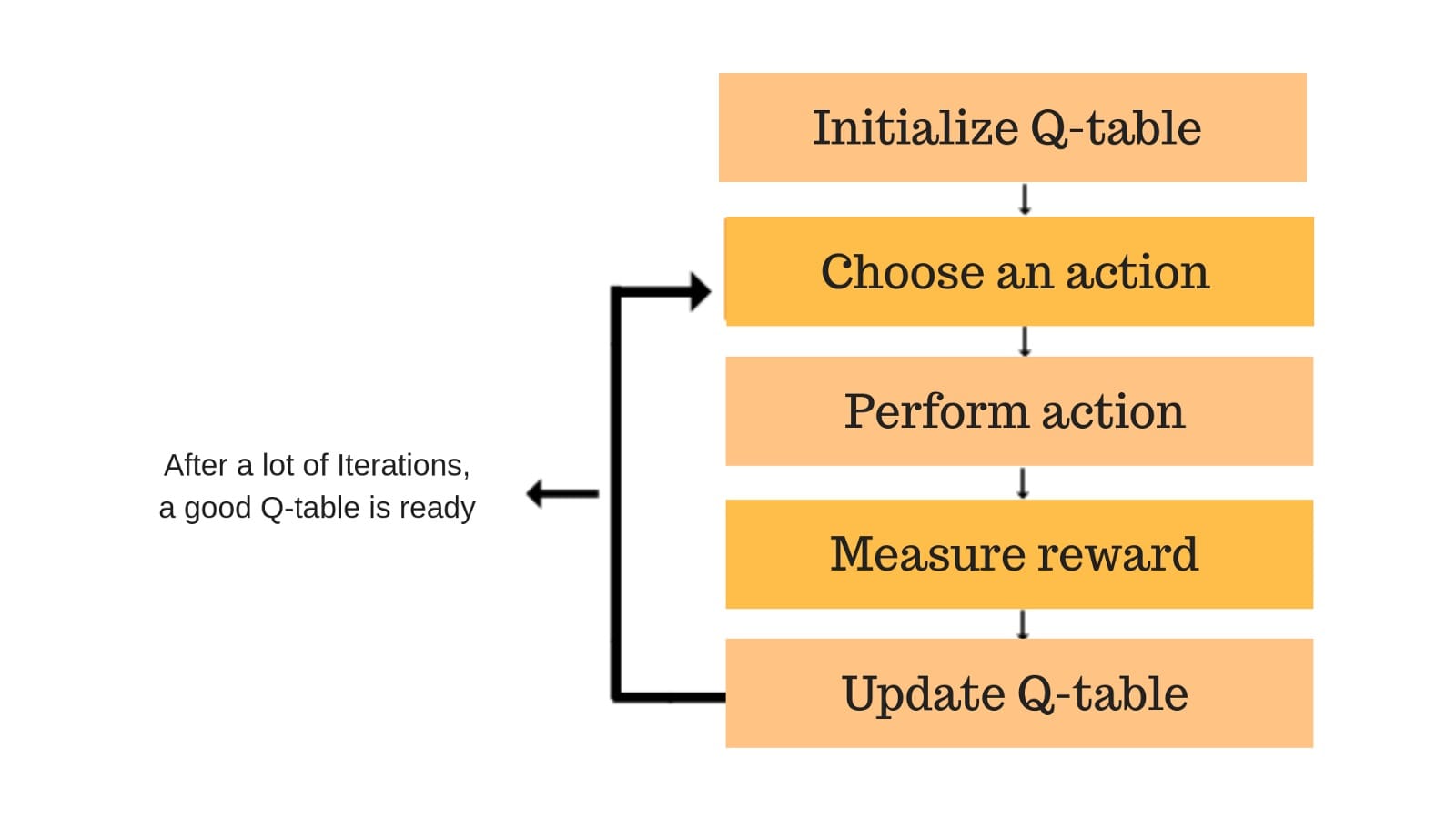
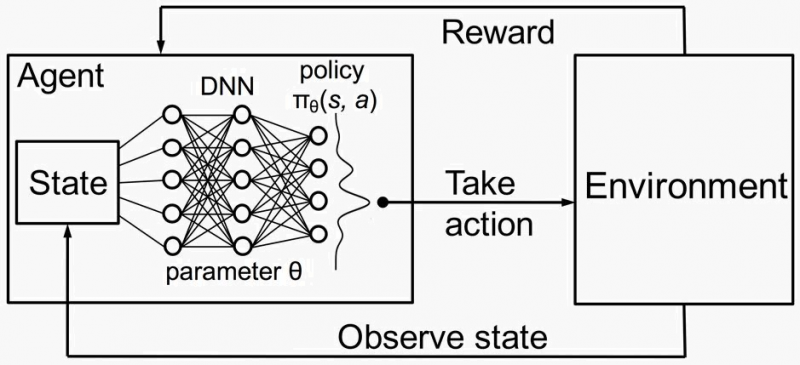
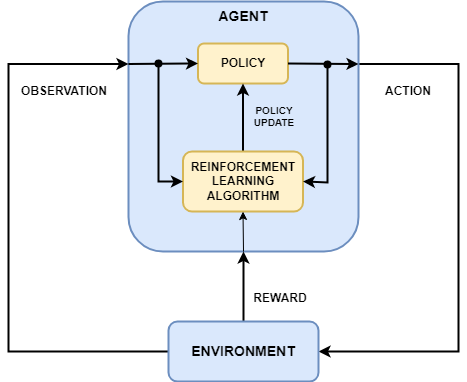
Q-learning is a model-free reinforcement learning algorithm that enables an agent to learn an optimal policy for decision-making. It works by estimating the Q-values (action-value function), which represent the expected cumulative reward for taking an action in a given state and following the best future actions. The agent updates Q-values iteratively using the formula: